
Development of abrasive water jet machining
Although waterjet cutting was initially only used for soft, low-hardness materials, the addition of abrasive particles to the cutting beam turned the water jet into a modern machining tool that could be used for cut for all materials. The new term Abrasive Waterjet (AWJ) - waterjet cutting using abrasives has been discovered and used for a variety of purposes in more than 50 industries worldwide. The question is, how can high-pressure water jets be directed safely and quickly without destroying their pipes? The answer is that they have researched and created a series of ceramic carbide composite tubes that significantly increase the operating life of the nozzle.
Comparison
Conventional Water jet machining
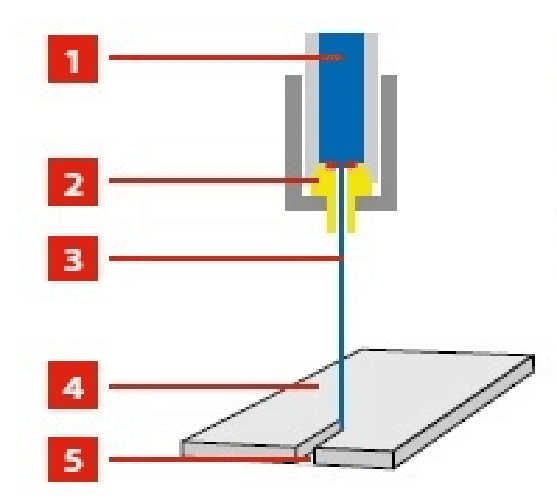
- 1 - High pressure water
- 2 - Nozzle
- 3 - Waterjet beam
- 4 - Workpiece
- 5 - Cut width
Abrasive Water jet machining
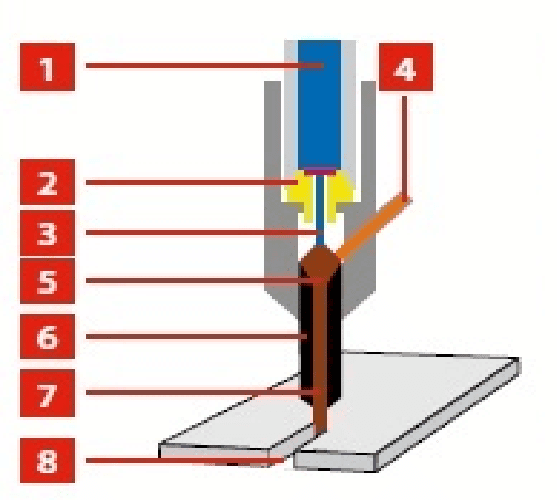
- 1 - High pressure water
- 2 - Nozzle
- 3 - Waterjet beam
- 4 - Abrasive loader (non-pressure)
- 5 - Mixing tube (vacuum tube)
- 7 - Water with abrasive particle nozzle
- 8. Cut width
How does it work?
Early waterjet cutting systems were controlled by tuning such as a mechanical protractor and G-code-coded NC system. But the shortcomings of traditional NC machine G-Code-based waterjet cutting already exist, as the accuracy depends on the changing speed of the nozzle as it runs to the arc interpolation positions. round, sudden changes, or complex profiles. Creating motion control systems to incorporate those variables became a major innovation for the top waterjet manufacturers in the early 1990s. People invented the OMAX software and developed the system for precisely positioning the water nozzle and setting the exact speed at every point on the jet’s putting stroke, using conventional PCs as the controller.
Most water jet cutters produce high-pressure water flow to cut the material through the high-pressure pump. There are two types of pumps commonly used to generate this high pressure. Water is then pushed along the high-pressure hose to the sprinkler. In the nozzle, water is concentrated into a thin beam by a small hole. This water jet is pushed out from the nozzle, cutting through the material by spraying it at speeds up to 2736 km / h. Here abrasive particles are fed into the tap through an inlet. The abrasive then mixes with the water in the mixing tube and is expelled at high pressure.
We Guarantee Successful Outsourcing
Best delivery performance, competitive pricing, better commercial terms, stable supplier base, control lead time
Effective and seamless workflow
With millions of parts delivered annually and serving more than 30 international customers, we are practicing the most advanced workflow to ensure the satisfaction of our customers and suppliers
-
part shipped annually7mil
-
Quality acceptance98%
Free consultation
Book an online meeting within 24 hours

