Introduction
Casting material in Vietnam is a foundation of modern manufacturing. Casting allows molten metal to be poured into molds and shaped into precise components. Unlike 3D printing, which dominates prototyping, casting remains the most economical and reliable solution for large-scale production. The process not only supports a wide variety of metals but also delivers products with durability, aesthetics, and cost efficiency. From machine parts to church bells, metal casting continues to shape industries worldwide.
The Casting Process in Vietnam
Step 1: Prototyping (Patternmaking)
Production starts with a prototype of the final product. Manufacturers use wood, plastic, metal, or sand to design the pattern. This model defines both geometry and size, ensuring the mold can reproduce accurate shapes.
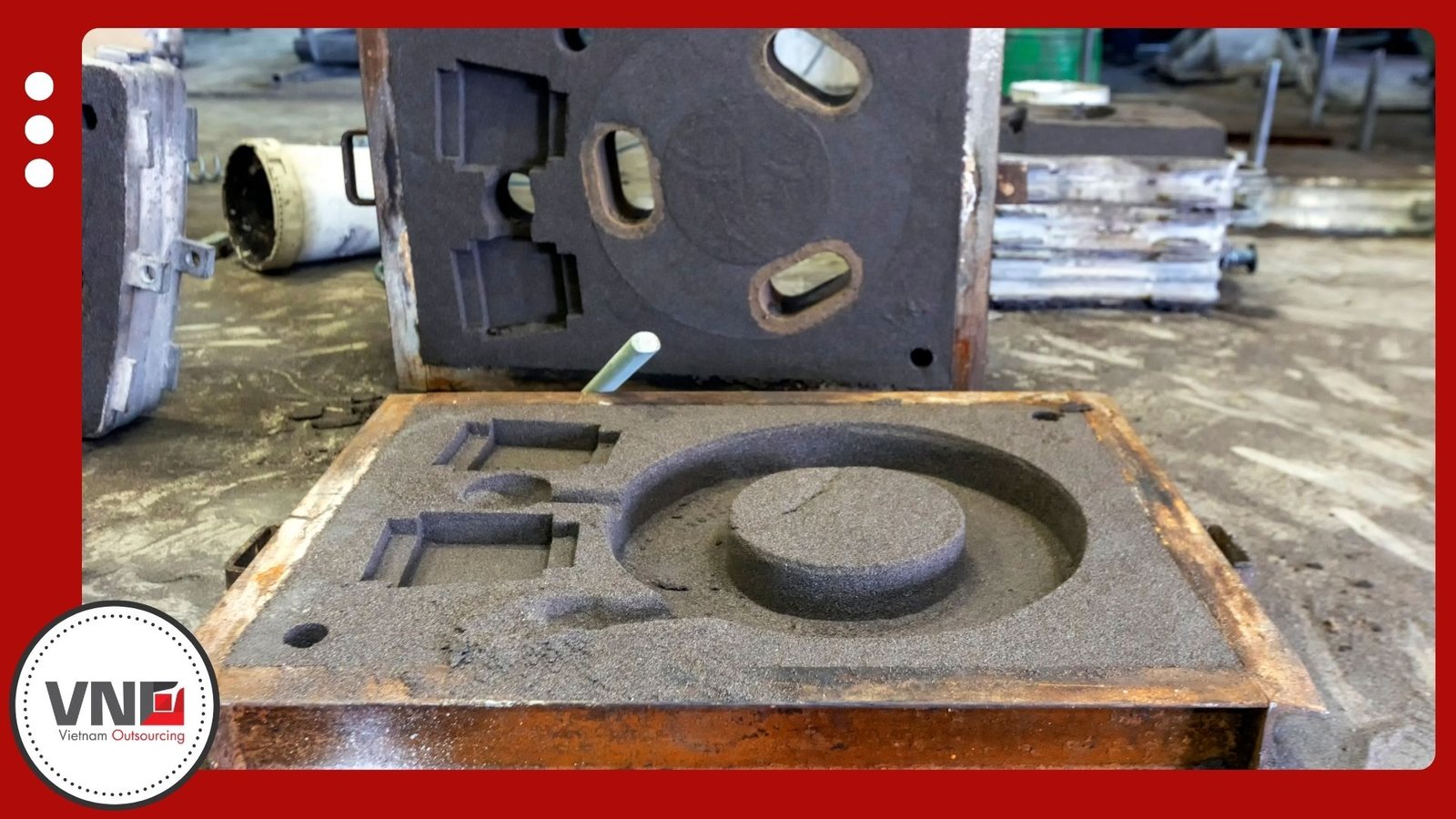
Step 2: Molding
Molds are then prepared for molten metal. Two main types exist:
Non-reusable molds (sand molds) that serve one casting cycle.
Reusable molds (metal molds) designed for repeated use.
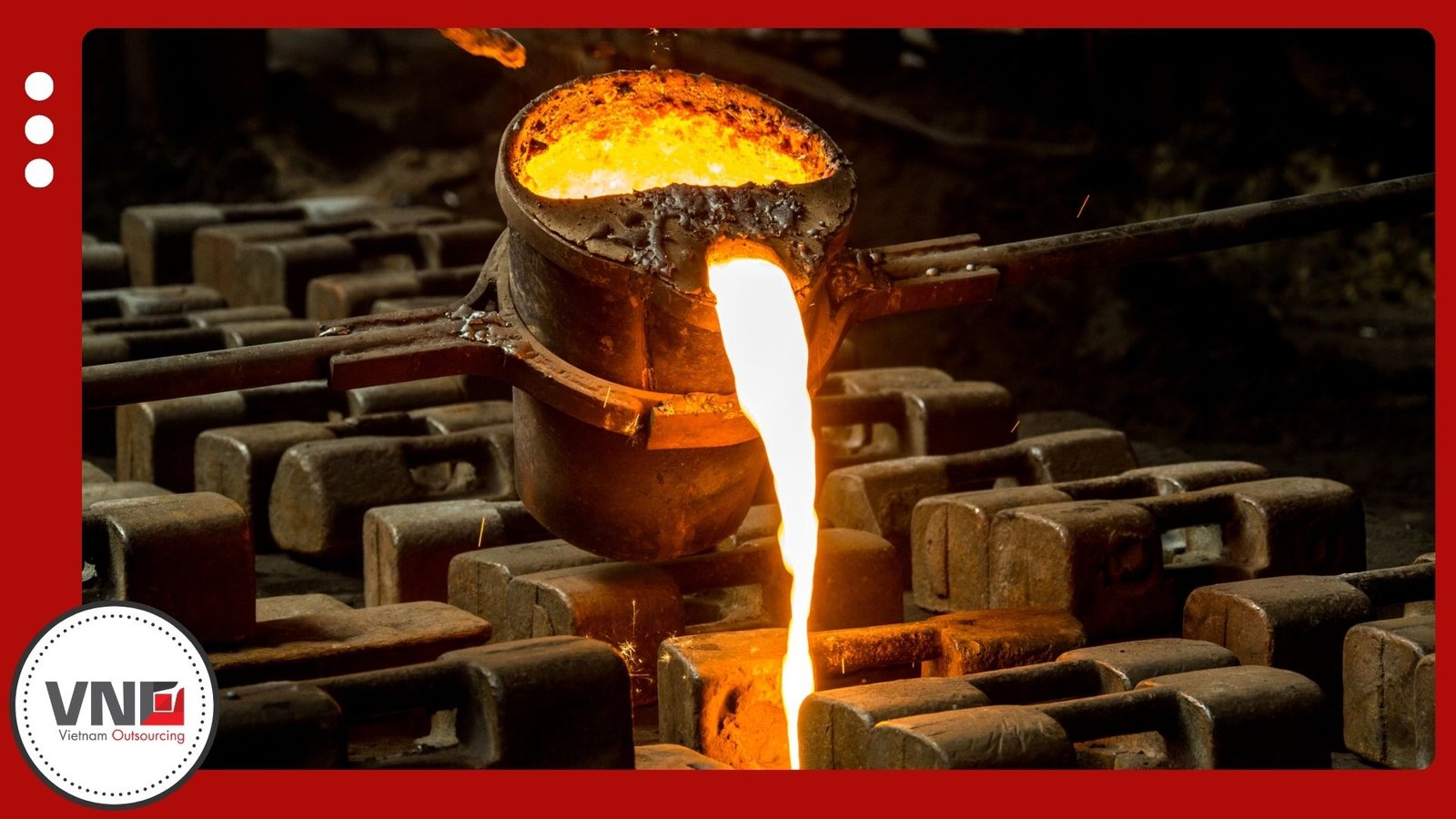
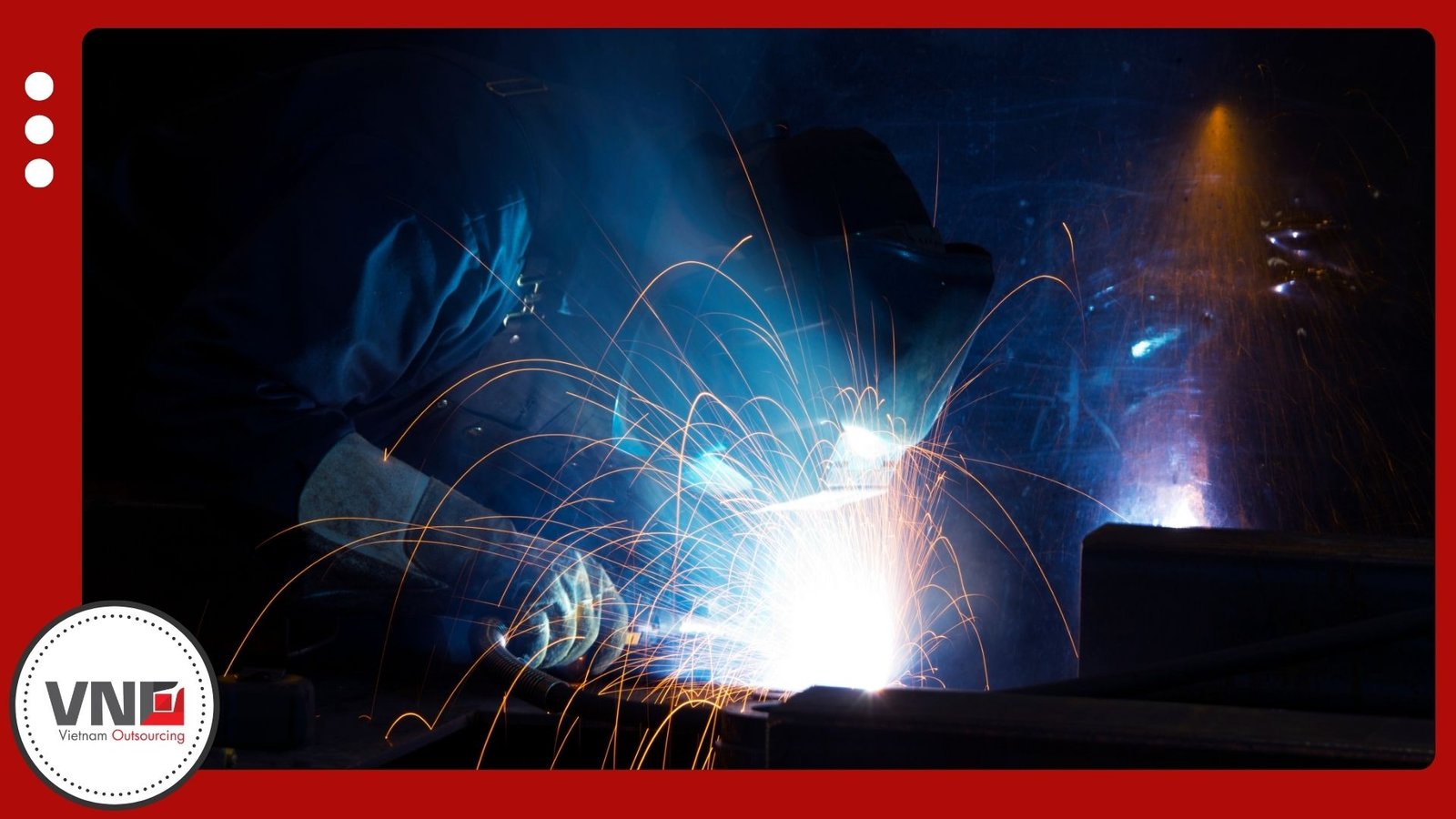
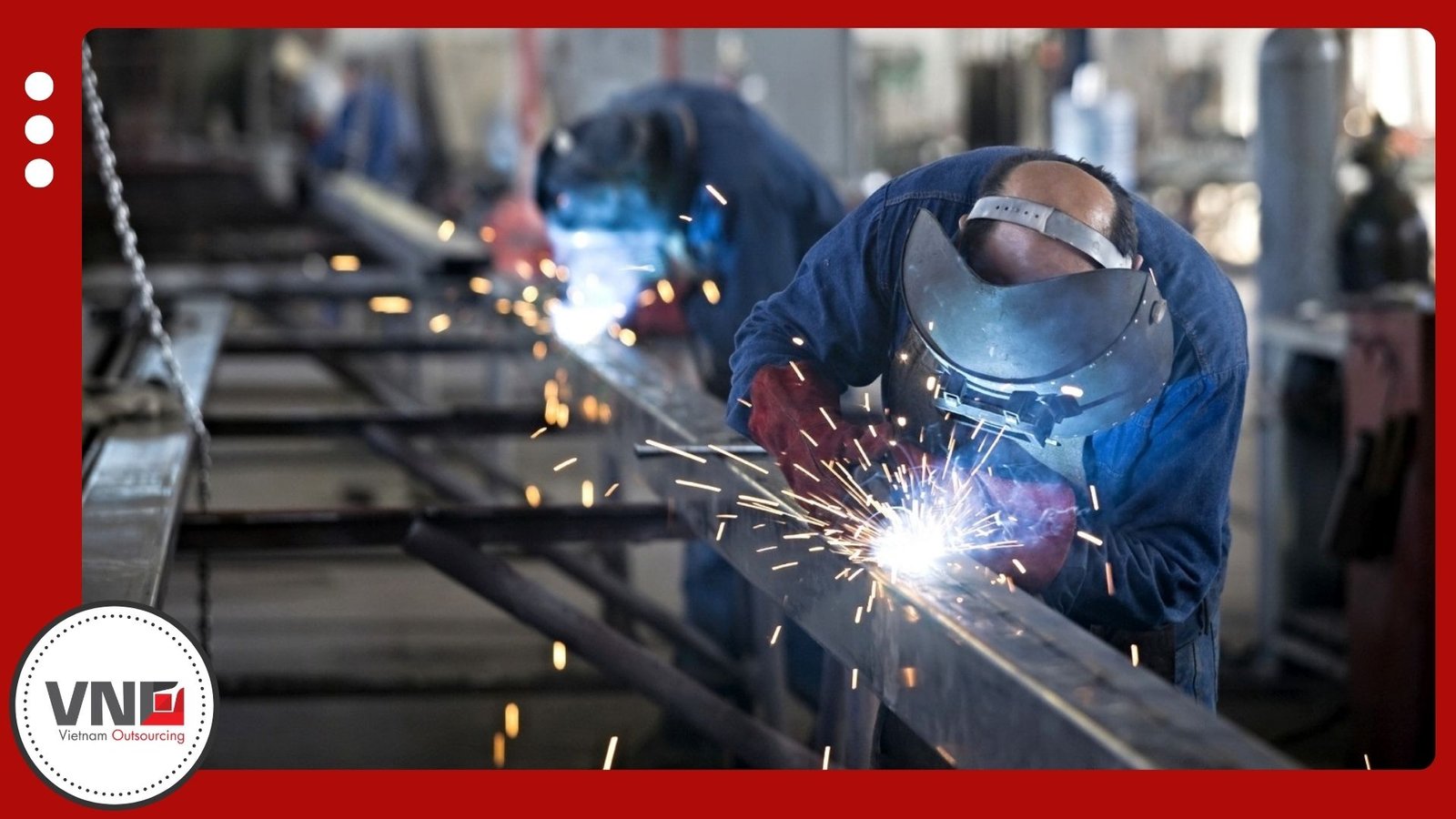
Step 3: Melting and Pouring
Furnaces heat metals such as aluminum, copper, steel, or zinc until molten. Workers pour the liquid metal into the mold cavity, where it fills every detail. Once cooled, the material solidifies into its final form.
Step 4: Shake-Out and Cleaning
After solidification, operators remove the casting from the mold. Sand is shaken out of sand molds, and excess material is trimmed away. The cleaned piece matches the original design with improved accuracy.
Step 5: Heat Treatment
Cast products often require additional strength or hardness. Heat treatment processes, such as quenching or tempering, enhance mechanical performance and extend service life.
Step 6: Inspection
Before delivery, each product undergoes strict inspection. Tests confirm both structural integrity and mechanical performance, ensuring consistency across every batch.

Types of Casting Material in Vietnam
Aluminum Casting
Aluminum offers light weight, corrosion resistance, and strong thermal conductivity. Vietnam die casting supplier uses it in automotive engines, solar panel frames, and consumer electronics. As a result, aluminum casting helps reduce product weight while maintaining strength.
Copper Casting
Copper provides excellent corrosion resistance and high electrical conductivity. In Vietnam, copper casting supports plumbing, electrical hardware, and decorative architecture. Moreover, alloys like bronze and brass expand its applications in machinery and art.
Zinc Casting
Zinc is easy to cast and supports intricate designs. It delivers durability, ductility, and smooth finishes, making it suitable for safety components, mechanical parts, and consumer products. Furthermore, zinc’s low casting temperature reduces energy costs.
Magnesium Casting
Magnesium is the lightest structural casting material. Its excellent strength-to-weight ratio makes it popular in aerospace and automotive parts. Therefore, Vietnamese magnesium casting offers global buyers lightweight, fuel-efficient solutions.
Steel Casting
Steel castings deliver toughness and high load-bearing capacity. In Vietnam, they are widely used for pipelines, construction machinery, and industrial equipment. In addition, steel casting adapts to both heavy-duty and precision applications.
Titanium Casting
Titanium combines low weight with exceptional strength and corrosion resistance. Vietnamese foundries produce titanium castings for aerospace, marine equipment, and medical implants. Although more expensive, titanium delivers unmatched performance in demanding environments.
Conclusion
The diversity of casting material in Vietnam makes the country a reliable global supplier. From lightweight aluminum and magnesium to high-strength steel and titanium, Vietnamese foundries provide versatility, quality, and competitive pricing. Combined with skilled labor and modern technology, Vietnam is positioned as a preferred destination for casting outsourcing.
Want to connect with reliable casting suppliers in Vietnam? Contact Vietnam Outsourcing (VNO) today to explore tailored solutions.