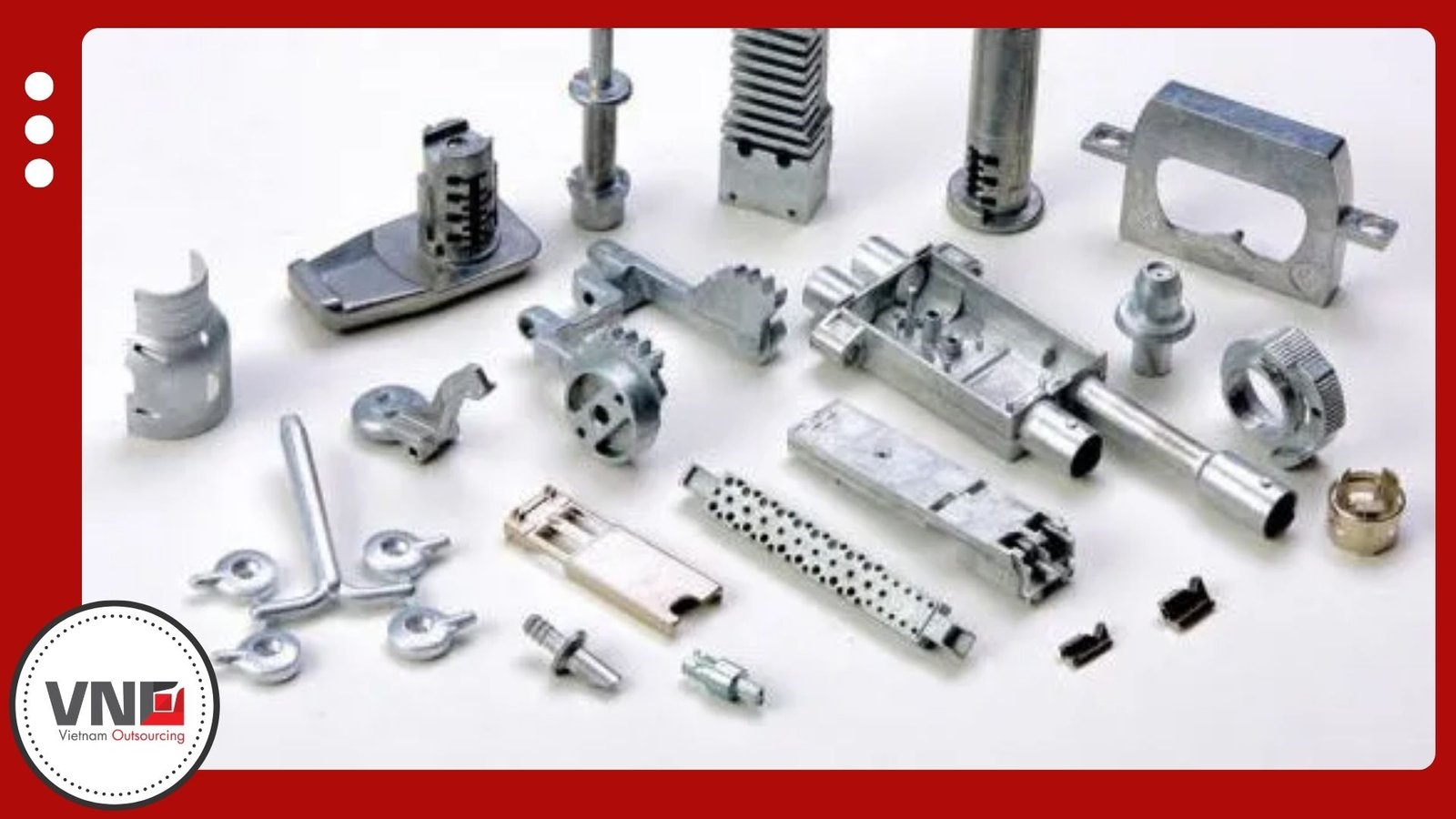
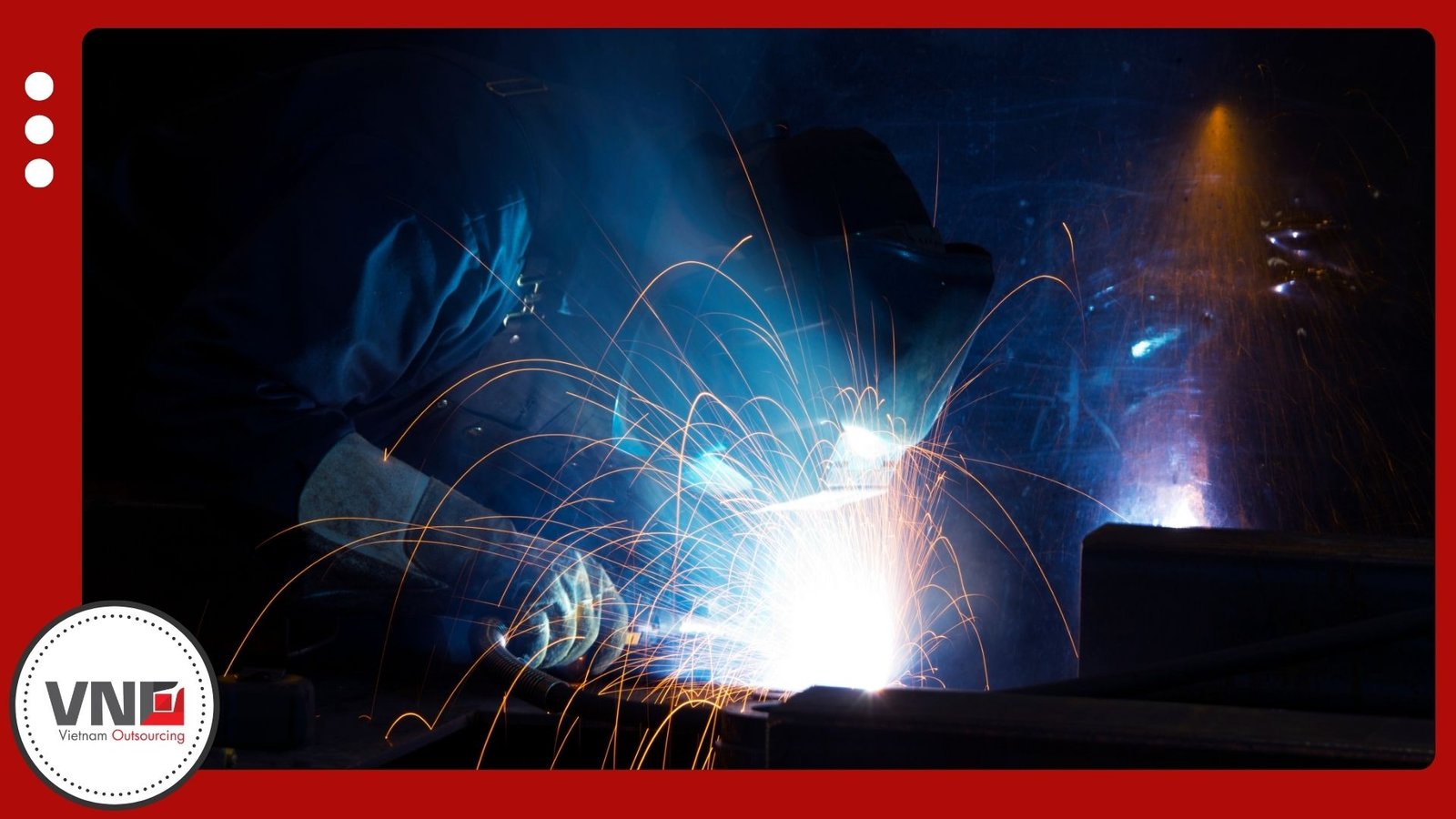
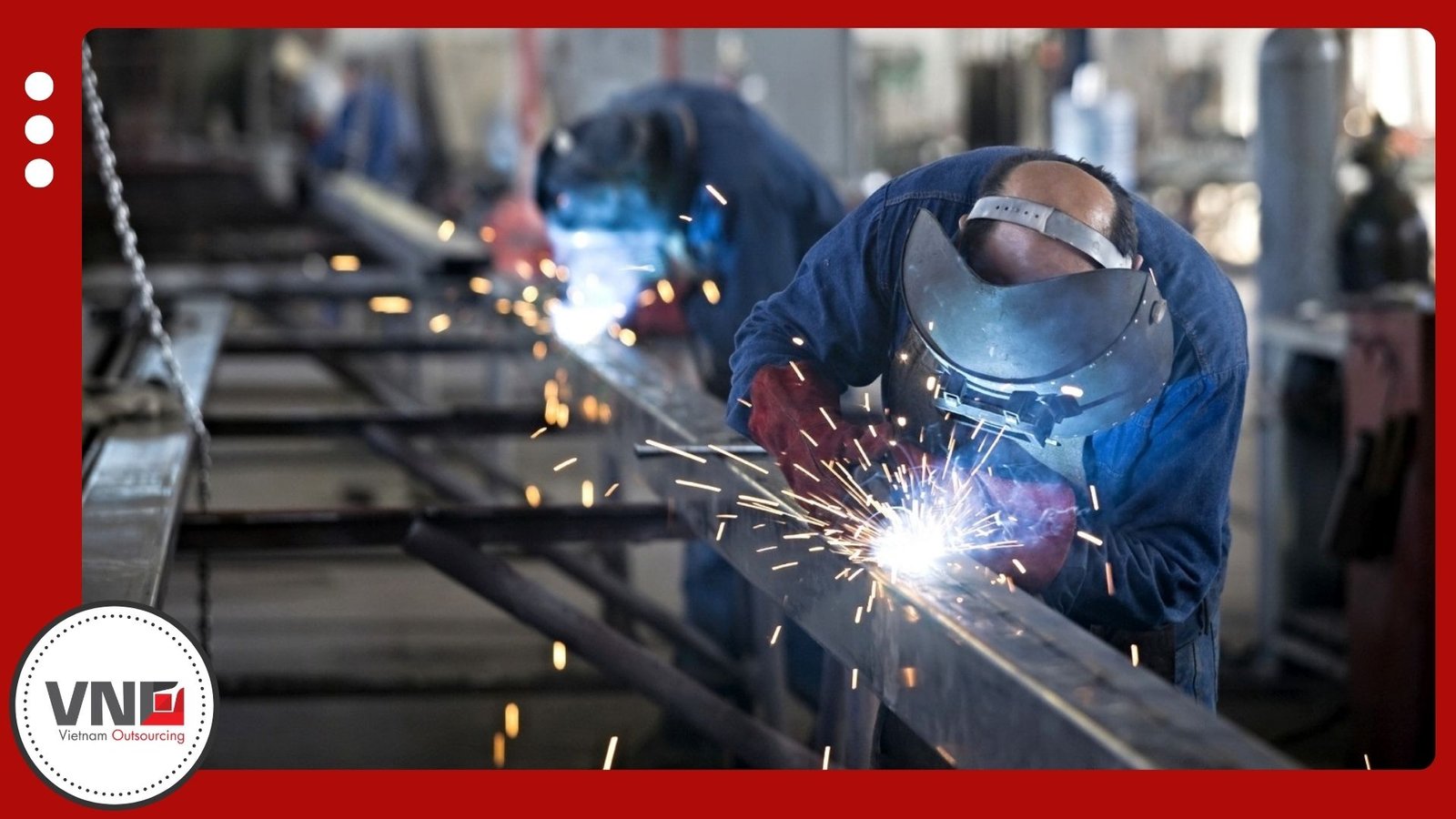
Introduction to Zinc Casting
Zinc casting is one of the most widely applied processes in manufacturing today. Unlike aluminum, zinc alloys melt at lower temperatures and require less pressure during production. This characteristic extends mold life and reduces costs, making zinc a practical choice of Vietnam die casting supplier for high-volume projects.
Materials Used in Zinc Alloy Casting
Common zinc alloys include ZAMAK 2, ZAMAK 5, ZAMAK 7, and ZA-27. Each provides strength, durability, and consistency, supporting diverse industrial requirements.
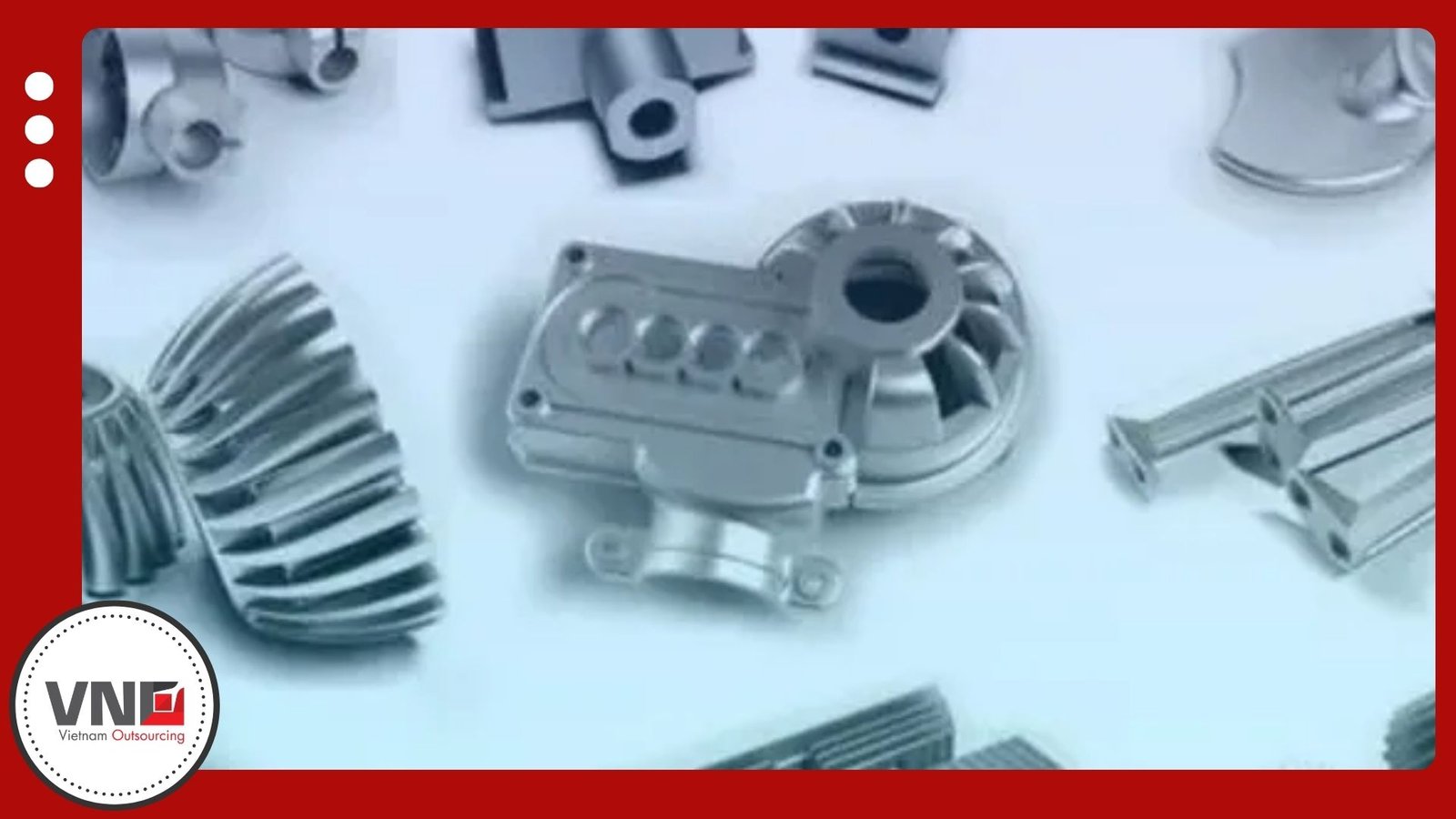

Applications in Modern Industry
Products made with zinc alloys are everywhere, from automotive and aerospace parts to wireless devices, HVAC systems, architectural fittings, and medical equipment. Manufacturers also rely on zinc for lighting fixtures, interior components, and security hardware.
Finishing Options for Zinc Components
Zinc-based castings adapt to many finishes, including:
- Blasting or sandblasting
- Polishing and brushing
- Powder coating or painting
- Electroplating with copper, nickel, chrome, imitation gold, or PVD
These options provide both protective and aesthetic qualities, allowing flexibility for different industries.
Key Advantages of Zinc Alloys in Casting
- Fast production: Hot-chamber methods increase efficiency while lowering costs.
- Durability: Zinc offers excellent impact resistance, often outperforming aluminum.
- Design flexibility: The material easily fills thin or complex molds.
- Smooth results: Castings typically require little post-processing thanks to reduced thermal shock.
Why Manufacturers Choose Zinc Alloys
Zinc die casting strikes the balance between affordability, strength, and versatility. By delivering long mold life, minimal finishing work, and reliable performance, it remains a vital process for sectors that demand both function and precision. For more knowledge regards to other material, read titanium casting.