Introduction
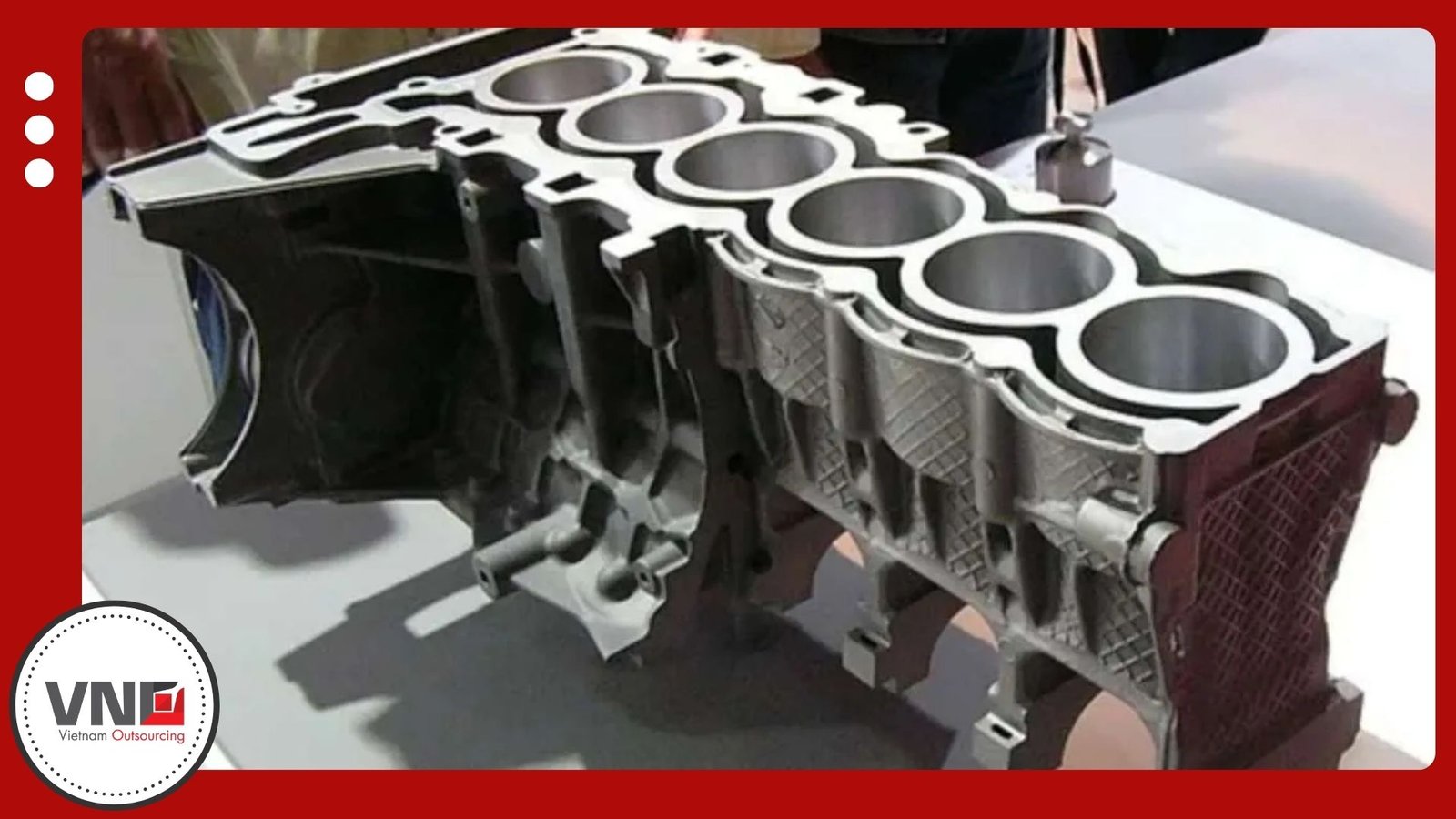
Titanium casting is one of the most advanced processes in metalworking. The metal’s strength, light weight, and resistance to corrosion make it essential for aerospace, marine, energy, and medical applications. However, titanium reacts easily at high temperatures, so Vietnam die casting supplier must control the process carefully to ensure consistent results.
Nature of Titanium Casting
Titanium reacts quickly with air, forming a thin oxide film that protects the surface. When it melts, titanium bonds with oxygen to create titanium dioxide (TiO₂), which can lower casting quality. Foundries avoid this issue by using graphite or ceramic molds. These materials resist chemical reaction, reduce defects, and deliver more stable outcomes.

Main Casting Methods
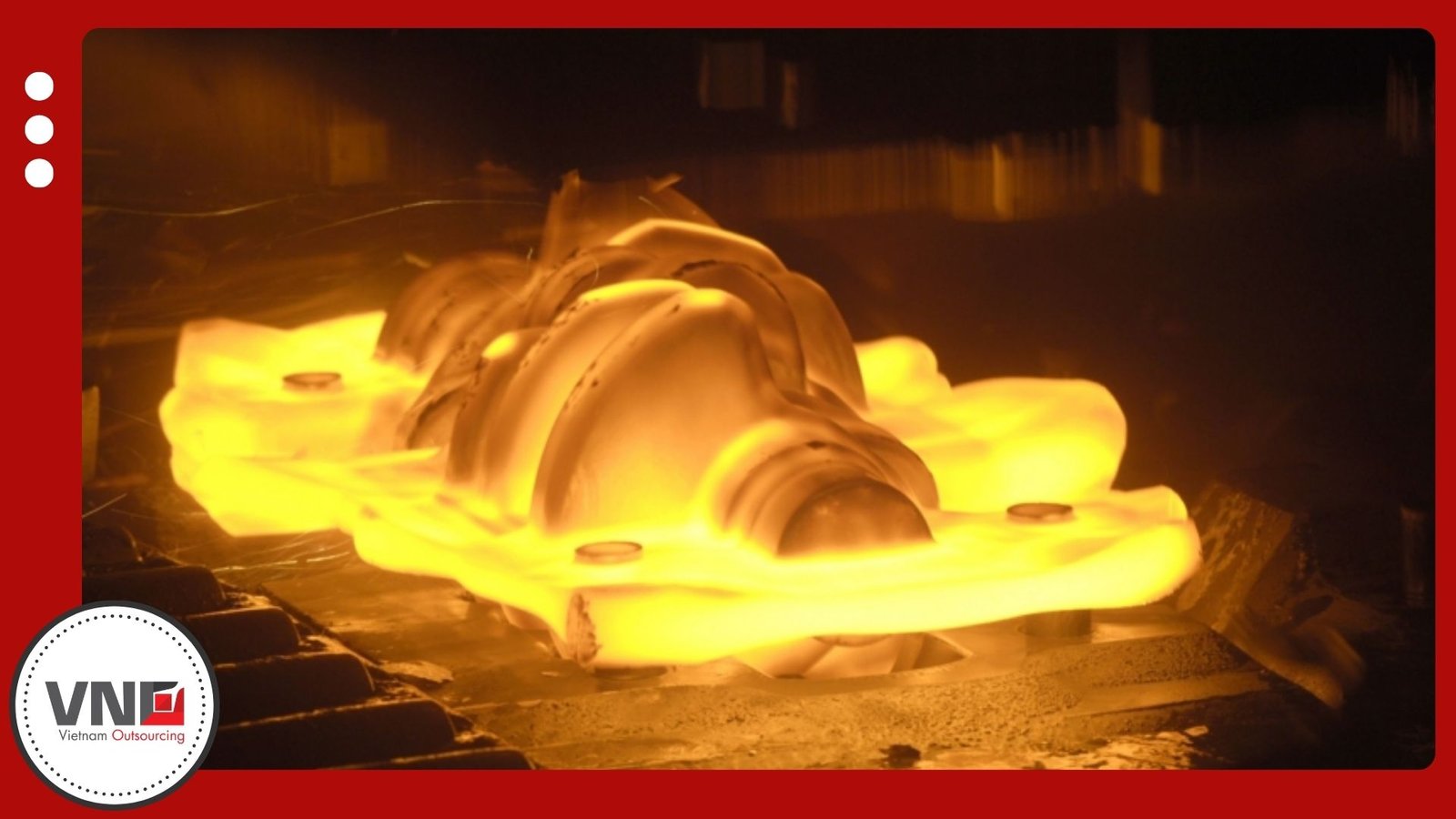
Graphite Mold Casting
Graphite mold casting works best for large or heavy parts. Because graphite resists high-temperature reaction, it helps manufacturers maintain consistent wall thickness and reliable quality. Aerospace housings, marine pumps, and energy equipment often rely on this method.
Ceramic Mold Investment Casting
Ceramic mold investment casting produces highly precise shapes. The ceramic shell captures fine details and creates smooth surfaces, which makes the method ideal for thin-walled or complex parts. Manufacturers commonly use it for turbine blades, medical implants, and automotive components.
Advantages of Titanium Casting
- Creates parts that are both strong and light, perfect for aerospace and automotive uses.
- Resists seawater, chemicals, and extreme conditions.
- Works safely in the human body, making it suitable for implants and surgical tools.
- Allows flexible design, enabling complex shapes that machining cannot achieve.
Applications of Titanium Casting
Titanium casting supports industries worldwide. In aerospace, it is used for jet engines, turbine blades, and structural frames. In medicine, it provides implants, dental parts, and surgical instruments. Marine applications include propellers, pumps, and corrosion-resistant valves. In energy, titanium castings serve offshore rigs, renewable energy systems, and power plants.
Conclusion
Titanium casting combines advanced molding techniques with one of the strongest metals available. The process delivers light, durable, and precise parts that meet strict performance demands. As global industries look for high-performance solutions, titanium casting continues to provide strength, reliability, and efficiency. For other characteristics of different materials, read zinc casting.